- Differences by partisanship
- Differences by age
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
Protecting the U.S. from terrorism and reducing the flow of illegal drugs are top issues overall, but Democrats and Republicans have very different priorities

Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to better understand Americans’ long-range foreign policy priorities. For this analysis, we surveyed 3,600 U.S. adults from April 1 to April 7, 2024. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology.
Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology.
Americans have a lot on their plates in 2024, including an important election to determine who will remain or become again president. But the world does not stop for a U.S. election, and multiple conflicts around the world as well as other issues of global prominence continue to concern Americans.
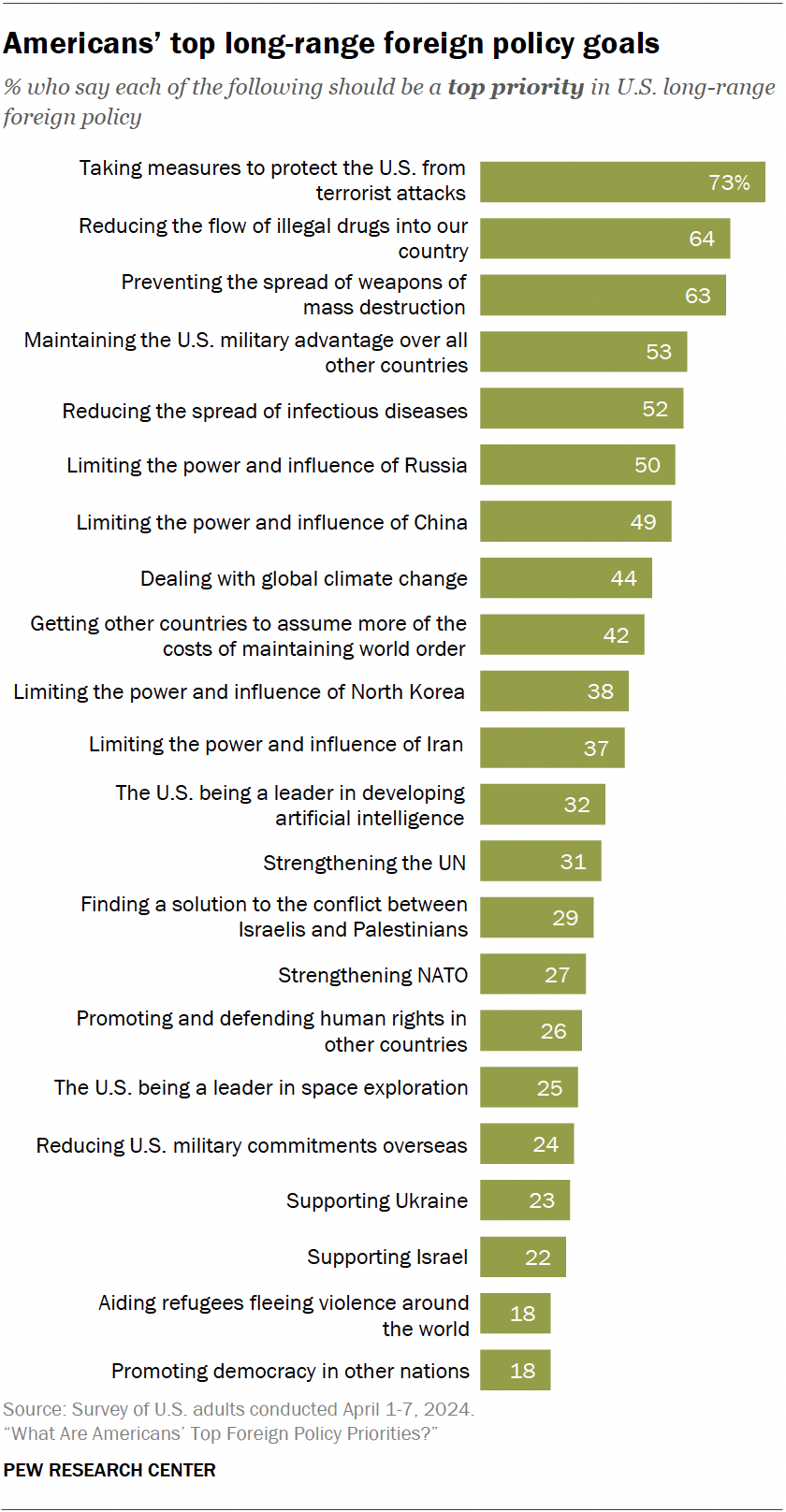
When asked to prioritize the long-range foreign policy goals of the United States, the majority of Americans say preventing terrorist attacks (73%), keeping illegal drugs out of the country (64%) and preventing the spread of weapons of mass destruction (63%) are top priorities. Over half of Americans also see maintaining the U.S. military advantage over other countries (53%) and preventing the spread of infectious diseases (52%) as primary foreign policy responsibilities.
About half of Americans say limiting the power and influence of Russia and China are top priorities. A recent annual threat assessment from the U.S. intelligence community focused heavily on those countries’ strengthening military relationship and their ability to shape the global narrative against U.S. interests.
Fewer than half of Americans say dealing with global climate change (44%) and getting other countries to assume more of the costs of maintaining world order (42%) are top priorities. The partisan gaps on these two issues are quite large:
- 70% of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents say climate change should be a top priority, while 15% of Republicans and Republican leaners say this.
- 54% of Republicans say getting other countries to assume more of the costs of maintaining world order should be a top priority, compared with 33% of Democrats.
About four-in-ten Americans see limiting the power and influence of North Korea and Iran as top priorities. (The survey was conducted before Iran’s large-scale missile attack on Israel on April 13.) And about a third say the same about the U.S. being a leader in artificial intelligence, a technology that governments around the world are increasingly concerned about.
When it comes to goals that focus on international engagement, like strengthening the United Nations and NATO or finding a solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, fewer than a third of Americans mark these as top foreign policy priorities.
Only about a quarter of Americans prioritize promoting human rights in other countries, leading other countries in space exploration and reducing military commitments overseas. And similar shares say supporting Ukraine (23%) and Israel (22%) are top issues.
At the bottom of this list of foreign policy priorities are promoting global democracy (a major policy push from the Biden administration) and aiding refugees fleeing violence around the world – about two-in-ten Americans describe these as top concerns. These assessments come amid a recent global surge in asylum claims. Still, in Center surveys, democracy promotion has typically been at the bottom of Americans’ list of foreign policy priorities, even dating back to George W. Bush’s and Barack Obama’s administrations.
Overall, a majority of Americans say that all 22 long-range foreign policy goals we asked about should be given at least some priority. Still, about three-in-ten Americans say supporting Israel (31%), promoting democracy (28%) and supporting Ukraine (27%) should be given no priority.

The long-range foreign policy priority questions were also asked in 2018 and 2021, and since then there have been some significant shifts in responses:
- Since 2018, the public has become significantly more likely to say limiting the power and influence of China (+17 percentage points) and finding a solution to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict (+11) are top foreign policy priorities.
- Americans have also increased the emphasis they place on limiting the power and influence of Russia, particularly in the wake of the Russian invasion of Ukraine (+8 points since 2021).
- On the decline since 2018 are strengthening the UN and aiding refugees (-8 points each), reducing foreign military commitments (-6), and promoting and defending human rights in other countries (-5).
- Preventing the spread of infectious diseases is down 19 percentage points since 2021 – during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic – and about back to where it was in 2018.
These are among the findings from a Pew Research Center survey conducted April 1-7, 2024.
The survey of 3,600 U.S. adults shows that foreign policy remains a partisan issue. Republicans prioritize the prevention of terrorism, reducing the flow of illegal drugs into the country, and maintaining a military advantage over other nations. Meanwhile, Democrats prioritize dealing with climate change and preventing the spread of weapons of mass destruction (WMDs), but also preventing terrorist attacks.

There are also stark age differences on many of the policy goals mentioned, but for the most part, young adults are less likely than older Americans to say the issues we asked about are top priorities. The exceptions are dealing with climate change, reducing military commitments overseas, and promoting and defending human rights abroad – on these issues, 18- to 29-year-olds are significantly more likely than older Americans to assign top priority.
Even with these priorities, foreign policy generally takes the backset to domestic policy for most Americans: 83% say it is more important for President Joe Biden to focus on domestic policy, compared with 14% who say he should focus on foreign policy.
Americans are even less likely to prioritize international affairs than they were in 2019, when 74% wanted then-President Donald Trump to focus on domestic policy and 23% said he should focus on foreign policy.
Differences by partisanship
Americans’ foreign policy priorities differ greatly by party. The largest divide, by a significant margin, is the 55 percentage point gap between Democrats and Republicans on dealing with global climate change (70% vs. 15%, respectively, see it as a top priority).
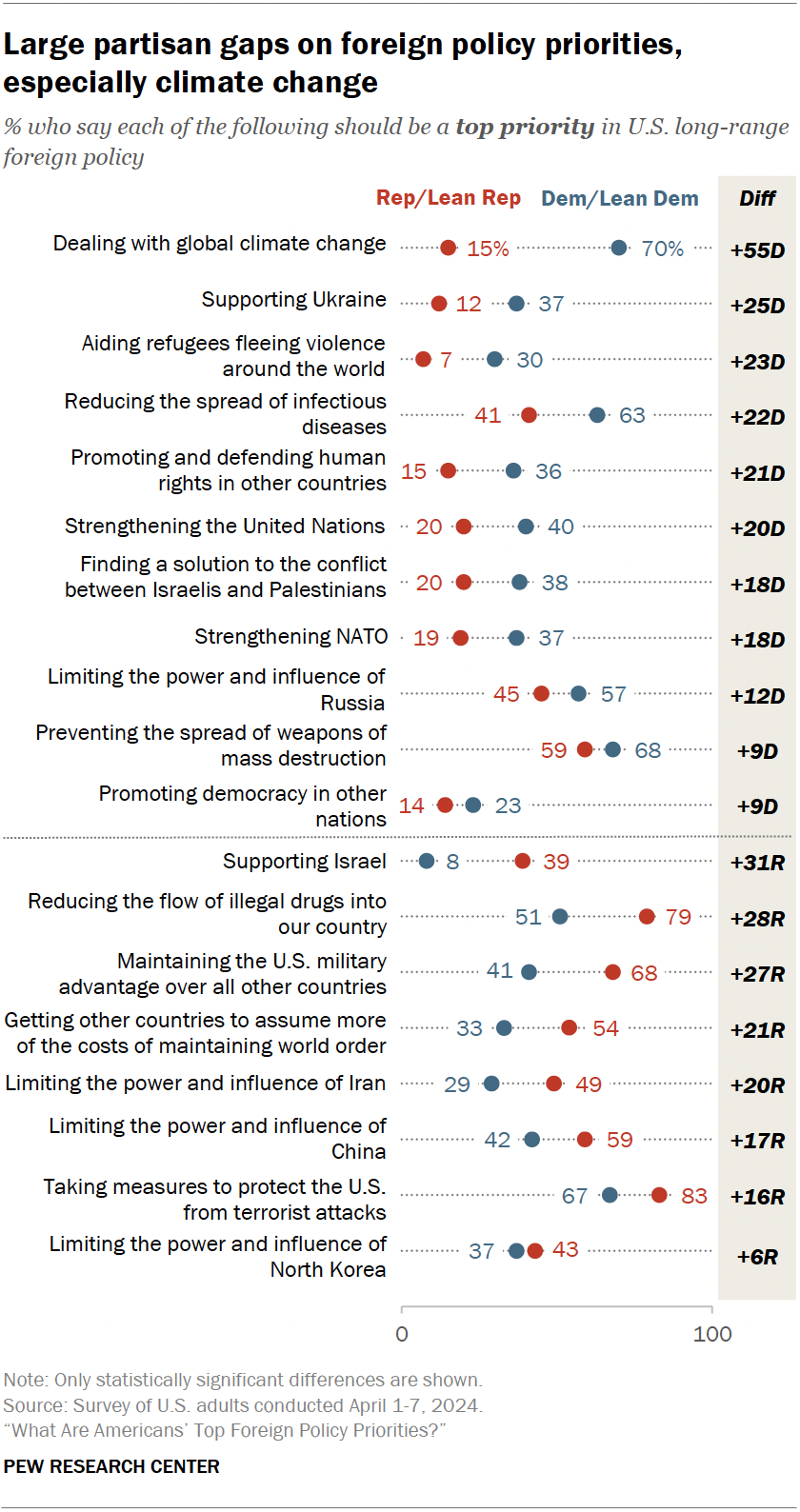
Supporting Ukraine, aiding refugees, reducing the spread of diseases, protecting human rights, and strengthening the UN are also issues on which Democrats are at least 20 points more likely than Republicans to prioritize. For example, 63% of Democrats say reducing the spread of infectious diseases is a top priority, compared with 41% of Republicans.
Republicans prioritize supporting Israel, reducing the flow of illegal drugs and maintaining a military advantage over other countries – among other security and hard power issues – significantly more than Democrats do. For example, more than half of Republicans (54%) say getting other countries to assume more of the costs of maintaining world order should be a top focus in foreign policy. Only a third of Democrats say the same.
The priority assigned to several issues is divided even further by ideology within parties. Take support for Israel and Ukraine as examples. Supporting Israel is generally a higher priority for Republicans than Democrats, but within the Republican Party, 48% of conservatives say it’s a top concern, while 18% of moderates and liberals agree. Previous Center research shows that conservative Republicans are especially likely to favor military aid to Israel.
Supporting Ukraine, something Democrats emphasize more than Republicans, is a top priority particularly for liberal Democrats (47%), while about three-in-ten moderate and conservative Democrats agree (29%). Democrats have also shown more willingness than Republicans to provide aid to Ukraine in its conflict with Russia.
Generally, the partisan differences on the importance of several foreign policy issues have gotten smaller since 2021, when most of these questions were last fielded. This is especially true for items related to the relative power of major countries, like the U.S. maintaining a military advantage and limiting the power and influence of both Russia and China.
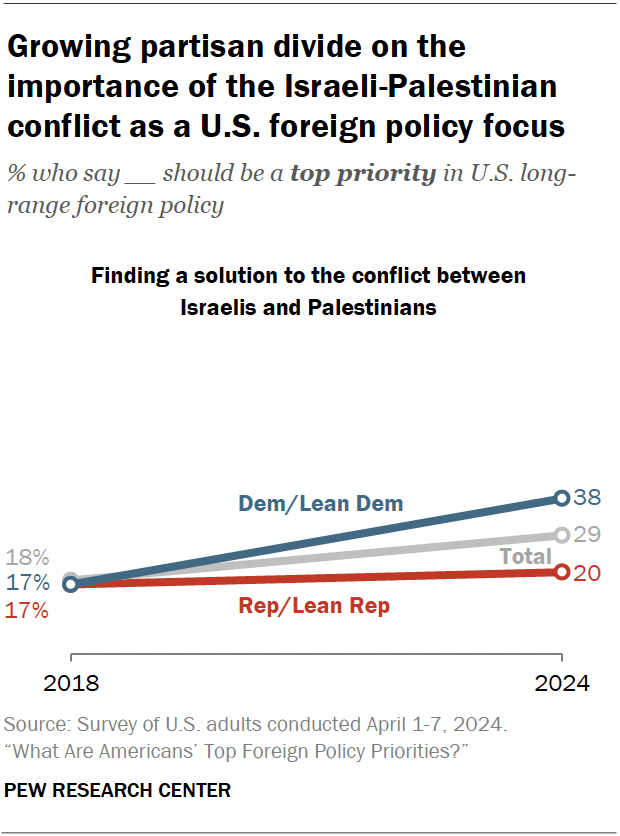
However, finding a solution to the conflict between Israelis and Palestinians – a priority that saw no partisan difference at all when it was last asked about in 2018 – has an emerging partisan gap today. The share of Democrats who call this a top priority has more than doubled, while the share of Republicans has changed little.
Differences by age
Age differences persist on foreign policy issues. Older Americans prioritize most of the issues we asked about at higher rates than those ages 18 t0 29.

On four issues, there is at least a 40 percentage point gap between Americans ages 65 and older and young adults ages 18 to 29. The oldest Americans are more likely to prioritize reducing the flow of illegal drugs, limiting the power and influence of China and Iran, and maintaining a U.S. military advantage.
Those in the oldest age group are also more concerned than their younger counterparts on an additional 11 issues, ranging from support for Israel to U.S. leadership in space exploration.
For their part, young adults are more likely to say dealing with global climate change, reducing U.S. military commitments overseas, and promoting and defending human rights in other countries should be top foreign policy priorities.
Even starker patterns appear when looking at partisanship within two age groups – adults ages 18 to 49 and those 50 and older.
Among Democrats, older adults place particularly high priority on supporting Ukraine, strengthening NATO, and limiting the power and influence of Russia amid its war with Ukraine. Older Democrats are also more likely than younger ones to prioritize preventing the development of WMDs, curbing the spread of diseases, strengthening the UN and promoting democracy around the world, among other issues.
Among Republicans, those ages 50 and older are more likely than those ages 18 to 49 to prioritize supporting Israel, limiting the power and influence of Iran and China, getting other countries to assume more foreign policy costs, reducing the amount of illegal drugs entering the U.S., preventing terrorism, and maintaining a military advantage.